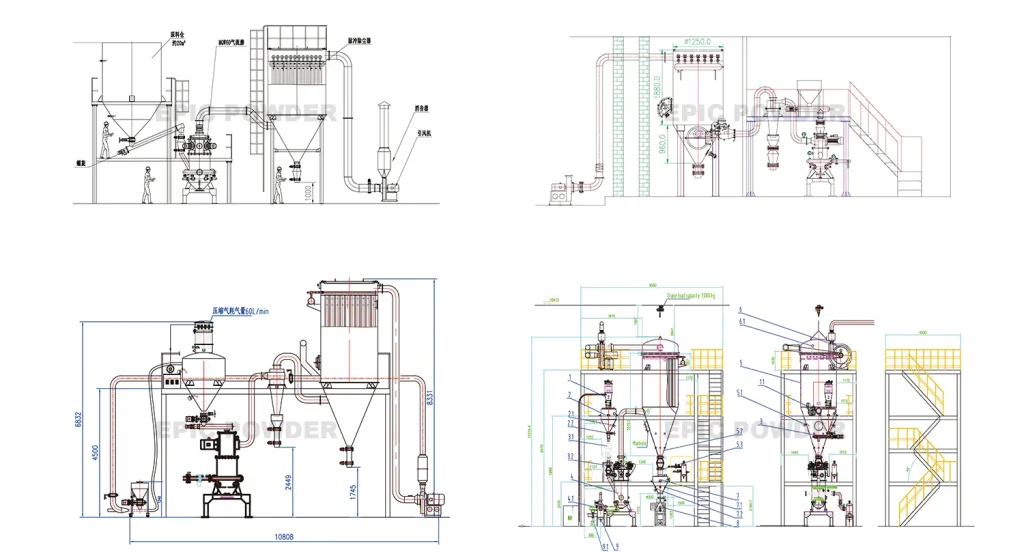
Spiral Jet Mills and Fluidised Bed Opposed Jet Mills
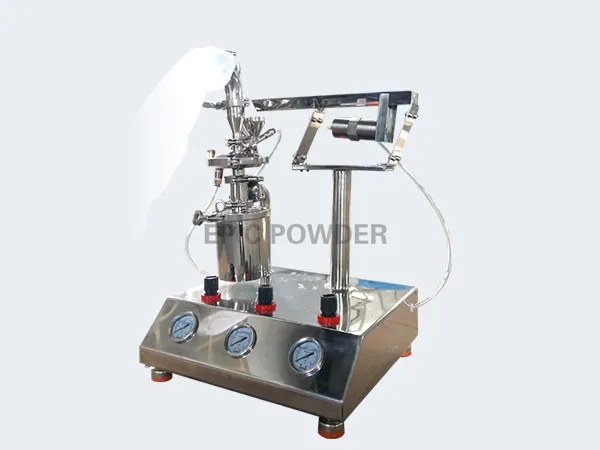

Introduction to Spiral Jet Mills
The most common type of jet mill is the spiral jet mill, in which the nozzles are arranged around the grinding chamber in such a way that the flow of the grinding gas spreads out in a spiral. The particles are then comminuted by mutual particle impacts. EPIC Powder has a spiral jet mill in its product range that is primarily used for high-quality pharmaceutical substances, e.g. antibiotics or fine chemicals. This is because the high demands on the purity and fineness of the products can be excellently implemented with this mill……
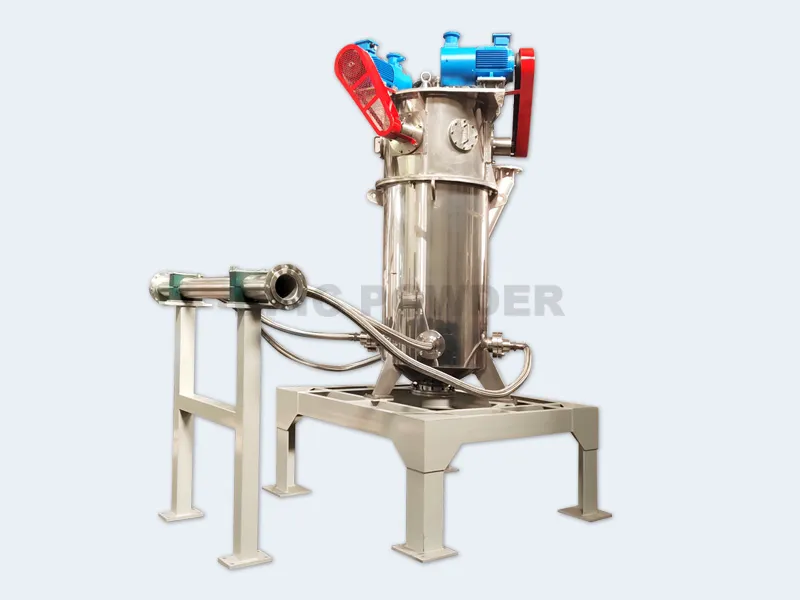

Introduction to Fluidised Bed Opposed Jet Mills
The fluidised bed opposed jet mill is the second most common type of jet mill. In this mill, the material to be ground is fed via a feed sluice. A product fluidised bed then forms in the grinding chamber, which is fluidised by the gas jets. From there, the particles enter the gas jets and are accelerated. They collide with each other again and again and are thus comminuted. A classifier wheel rejects those particles that are still too large and transports them back into the fluidised bed. The particles that are fine enough are separated from the grinding gas by a separator or dust filter. Fluidised bed opposed jet mills are also suitable for very hard products such as minerals, glass or ceramics. Temperature-sensitive products such as toner or wax can also be ground with them……
EPIC Jet Mill Machines - Top 5 Micronizer for 1-30μm Powder (2024 OEM Supplier)
How Fluidized Bed Opposed Jet Mill Works? | EPIC Micronizer Expert